August 12, 2021
YouTube & Display Campaigns Now Included in Google Ads Attribution Models

Let’s say you just started a hip new pizza restaurant that serves top-notch woodfired pizza. You have to compete with the local major pizza delivery chain, as you, too, offer pizza delivery around your restaurant. You have heard about how advertising on the Google Display Network (GDN) is a great way to market to a specific audience and get your brand out there. There are an infinite number of targeting combinations to take advantage of; for example, you could target just men in the state of Georgia between the ages 25 and 34 that are browsing sites related to pizzerias.
While there are countless ways to target specific people, personas, or businesses, one very effective targeting method, radius targeting, is widely under-used. Implementing radius targeting is a unique method to narrow your focus on a very specific location through the GDN, ensuring your ads reach the right people at the right time and place.
Radius targeting is a more advanced method of narrowing down the scope of your targeting to focus on a specific region around a certain focal point. You might know already that you can target specific countries, cities, regions, and postal codes, but radius targeting allows you to narrow down targeting to as small as one kilometer or one mile around a specific address or set of coordinates.
You can select any point on the map to be your radius focal point by typing in the address or coordinates. Alternatively, you can find the exact spot by browsing the map and using the blue pin to mark that spot. This can be a handy tool to use when you do not know the exact coordinates to narrow down to a closer, one-mile radius target.
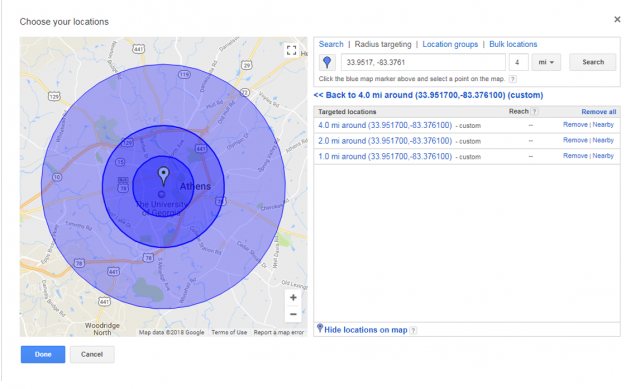
Radius targeting is commonly used by local business to target people around their specific store locations to drive additional foot traffic. However, there are other uses for radius targeting that go beyond this to target more specific personas, leading to more account-based marketing.
Here are a few examples of how using radius targeting on the GDN can be effective in reaching the right people:
Scenario 1: Radius targeting is perfect if you have a physical store location and want to drive sales close to you, similar to the pizza example above. If you don’t want to target an entire city, you can set your radius targeting to ten miles around the precise location of your pizza shop. Then you can craft ads that will set you apart from the local chain pizza delivery restaurant, perhaps highlighting the quality of your pizza, offering a promo code for first-time purchasers, or highlighting an event at your restaurant. As people around your shop browse the web, they will be exposed to your company, and you will extend your advertising reach to a specific group of people who are interested in what you offer.
You can also use radius targeting for a specific location to tier bids based on how close someone is to the epicenter of your targeting. For example, targeting people within a one-mile radius with a plus 50 percent bid modifier, plus 30 percent for a five-mile radius, and plus 15 percent for a ten-mile radius. This way, you can control bids for more valuable traffic based off how close they are to a certain location.
Scenario 2: You are a large clothing company that specializes in making university apparel. Your target audience is college students and people around the universities. In order to acquire new customers, you turn to the GDN and radius targeting. Since you don’t want to just target the college town, but also the surrounding area, you narrow down a 15-mile radius around a specific university. You can then create custom banner ads with that school’s name, colors, and mascot and show a specific shirt that is only relevant to that school. This process can then be repeated for all the schools you make apparel for, with each school in its own campaign.
With radius-targeting, you now have hyper-relevant ads to market to college students in the area, and you’re able to see a clear picture of performance by school. Now you’ll no longer have to use general ads; instead, you can show the right school merchandise to the right group of people, closest to the university.

Scenario 3: You are a B2B company on the rise, having a fairly large client base. You have a wish list of 25 big companies that would be large accounts to add to your client base, not only for additional revenue from their business, but also to be more reputable with bigger clients. You want to use the GDN to target these specific companies and get in front of the right employees at the company to showcase the value of your software.
Using radius targeting, you can look up the coordinates of these 25 businesses and target 1 mile around their main office. You can have separate campaigns for each of these companies to gain deeper insight into which areas you’re showing ads to more often. Using radius targeting here pushes your brand in front of employees and decision makers at those companies. Plus, once leads are received from these campaigns, you can prioritize them since they are likely to be leads from your targeted companies.
Radius targeting has numerous use cases that will ensure you’re getting in front of the right audience. Since you know more about the specific people you are targeting, you can show hyper-targeted ads to those people at whatever stage of the purchase process they are in. While not mentioned above, you can also overlay remarketing audiences along with radius targeting to even further nurture customers through their purchase.
Implement radius targeting in your account if you want to have the highest amount of geographical control, want to target a very specific group of people, or want to get in front of key stakeholders at a company to make people know you’re the real deal. If you need help figuring out your targeting strategy, contact our team for an analysis.
